TAX CONSEQUENCES OF BREXIT FOR BRITISH PROPERTY OWNERS IN SPAIN

We are near the end of the transition period established within the BREXIT for British citizens resident in Spain, which ends on 31 December 2020. There are many tax consequences for British citizens in Spain but for now we are only going to focus on British citizens with assets in Spain. For example pensioners or owners of a second home. From the perspective of trade or the movement of British citizens in Spain for work reasons, the tax and bureaucratic consequences of Brexit are higher, even though we will not cover that in this article. However, we will also briefly address the process to obtain Spanish residency. This because during the past few months we have witnessed many police stations becoming overwhelmed and unable to meet the many requests for appointments for British citizens and their family members to obtain a residence permit in Spain. This procedure was approved as part of the transition period set to end on the 31st of December 2020.
Over the last few weeks of 2020, it has been impossible for many British citizens to make an appointment at the police station in the province where they live and this also applies to the province of Malaga in Andalusia. This has led many British citizens resident in Spain or about to move to Spain starting 2021 without a residence permit.
What will be the situation of British citizens resident in Spain after BREXIT?
Well, these British citizens will have to apply for a residence permit after the final Brexit on the 1st of January 2021, just like any other citizen from a third country outside the European Union. We recommend that first of all these citizens register with their city hall as soon as possible and also request a S1 form from the United Kingdom to prove that their healthcare costs in Spain will be covered by the United Kingdom. After this, the easiest thing to do is to contact a law firm or administration company that can advise you and help you with the process, as it will be complicated to do it on your own. It is very important not to delay and do this as soon as possible, even though it is true that there is currently a lot of uncertainty about the procedure in question, as the negotiations with the European Union remain open.
How will the status of British citizens change after 1 January?
British citizens will be able to travel to Spain and stay for up to 90 days within a 6-month period, consecutive or not, without having to obtain a visa. They could even be required to prove their financial capacity to cover their stay in Spain, as is the case with travellers from countries outside the European Union. If they wish to stay longer, it is very likely that they will have to apply for a visa or work permit, even though this has not been defined yet since the negotiations remain open.
What will happen with the British driving licence?
From 1 January 2021, the general regulations will apply and British driving licence will be valid to drive in Spain for six months counted from the owner’s entry in Spain or from the date that legal residence is obtained. They will need to exchange their British driving licence for a Spanish one to continue driving in Spain after those six months.
How will Inheritance Tax change after Brexit on the 1st of January 2021?
As we explained in detail in an earlier article about inheritance tax, fortunately, from 1 January 2019, citizens not resident in the European Union are able to obtain the same tax benefits and bonuses for Inheritance Tax as European citizens. Therefore, the application of Inheritance Tax and its consequences would not change for British citizens.
Potential future Inheritance Tax when buying a home in Spain
When considering the purchase of a home in Spain, as the regulations applicable to this tax depend on the autonomous community where the property is located, a very important matter is to consider which autonomous communities have a higher and a lower inheritance tax, before making such investment(s). For instance, British nationals are the main buyers of homes in Spain. Alicante (Valencian Community) and Malaga (Andalusia) are the two main locations for foreigners to buy a home in Spain but. However, when it comes to Inheritance Tax, there are big differences between one community and the other. The Valencian Community has the third highest Inheritance Tax in Spain, while Andalusia has the third lowest, according to the General Economists Council of Spain, in their taxation study for 2020. This means that, when thinking about that tax, Malaga has a much cheaper rate of Inheritance Tax than Alicante.
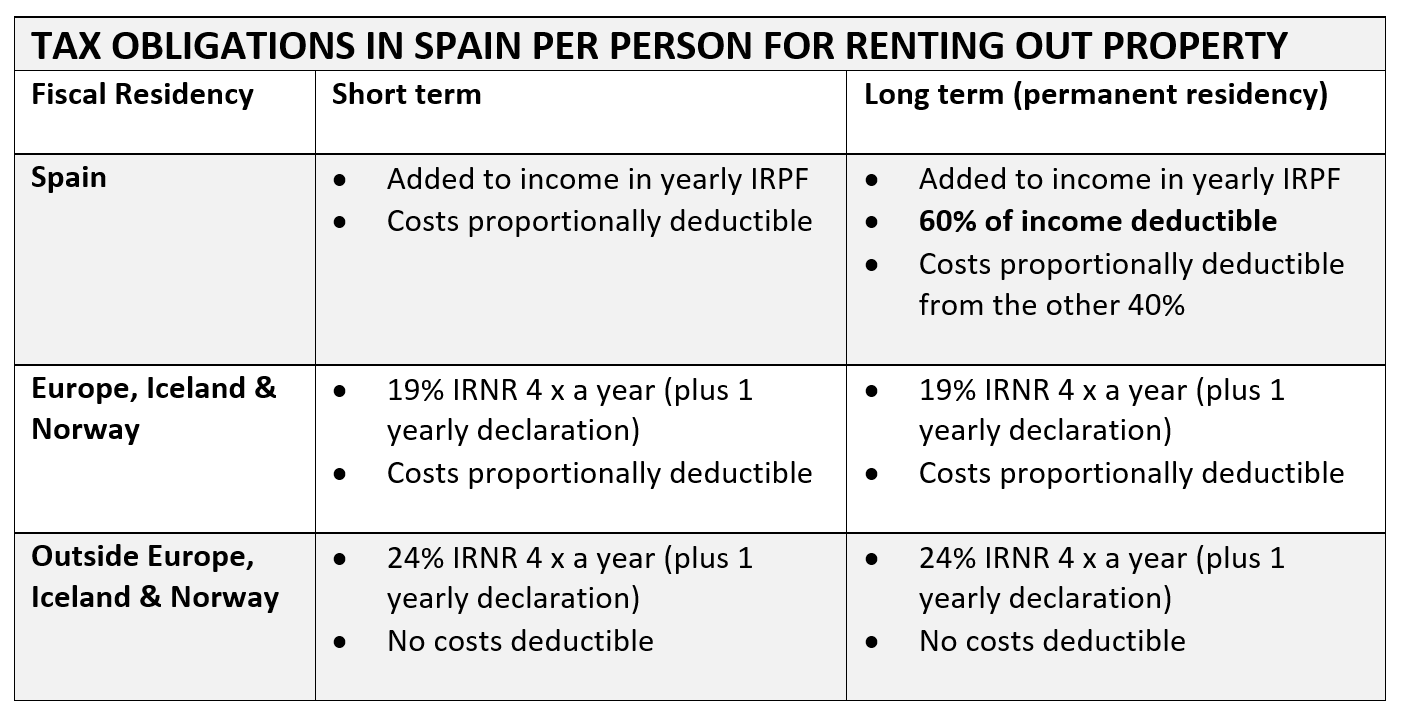
What happens to taxes on profits obtained from renting out my home in Spain?
If you bought a home in Malaga as an investment, for instance, and you use it for holiday rentals as a citizen of the European Union, the profit obtained from such rental would be taxed at 19% through their IRNR income tax for non-fiscal residents with a house in Spain. Many expenses can be deducted: mortgage interest, repair and maintenance costs for the property, electricity, insurance, etc. However, once you are considered a citizen not resident in the European Union, it will be taxed at 24% and no deduction for property expenses may be applied.
Estate Tax or Wealth Tax on my properties located in Spain
Estate Tax or Wealth tax also apply to assets and rights that non-residents have in Spain. As this tax has a minimum personal exemption threshold of 700,000 euros over the minimal fiscal value, all non-residents -in the EU or outside it- with assets of a lower value would pay nothing. The main difference in terms of EU and non-EU citizens lies in the fact that EU citizens can apply the regulations of the autonomous community where most of their assets are located. However, non-EU citizens would have to follow national regulations instead of those of the autonomous community where the assets are located. If we compare the tax rates in Andalusia to the national ones in terms of estate tax, the national rate of estate tax is somewhat lower. Therefore, applying national regulations does not always entail a greater tax liability.
The actual impact of that tax is non-existent for most non-residents due to the minimum fiscal value of 700,000 euros applied per person. This is why it is recommended that, if you are thinking about luxurious purchasing a property in for example Marbella on the Costa del Sol, it might be interesting to put the property in more than one name to profit from this exemption. Still, estate tax could have a high impact for those with high-value assets in Spain or considering the purchase of luxury properties.
How will Brexit affect the sale of my home in Spain?
The tax rate on capital gains obtained from selling the property stays at from 19%. The withholding (down payment) of the Capital Gain Tax that a buyer must apply to a non-resident seller to pay the amount at the Tax Agency in Spain will continue to be 3% of the purchase price. This percentage is the same for EU citizens and non-EU citizens.
Will Brexit affect the ITP transfer tax on the purchase of a home in Spain?
No, it will not. The property ITP transfer tax paid in Spain for the purchase of second-hand homes do not vary for EU citizens and non-EU citizens, for which reason, from 1 January 2021, it would not lead to greater expenses for British people. The same counts for the 21% VAT tax and documented legal acts (AJD tax) paid for new off-plan properties. The ITP tax depends on the autonomic region. For instance, in Andalucia a house buyer pays 8% ITP transfer tax over the purchase price up to € 400.000, until € 700.000 it´s 9% and after this the ITP will be 10%. To calculate the ITP tax on more expensive houses for a married couple it´s important to take into account if the couple is married in community or separation of goods.
Is the double-taxation agreement in force between Spain and the United Kingdom important?
Yes it is. The main purpose of this double-taxation agreement is for a British national living in Spain or a Spanish national living in the United Kingdom to be able to work and invest in those countries without having to pay twice for the same thing. This agreement will remain in force and is unaffected by the United Kingdom leaving the European Union. This agreement, which came into force on 12 June 2014, contains special clauses that exempt certain public pensions paid by the British government from taxation in Spain, as they can only be taxed in the United Kingdom. Likewise, this agreement protects residents national of either country from being taxed twice on income from capital gains and dividends. Income tax for non-residents, company tax, personal income tax and estate tax are covered by this agreement, for which reason these aspects should not be taxed twice in both countries.
Potential changes in the future for British house owners
Over the next few weeks, there will surely be changes affecting British nationals as it is very likely for the negotiations to change certain important aspects. However, on the date this article is posted (22 December 2020), little is known. We advise that, if you have any doubts, you contact and obtain legal or tax advice from a lawyer or company specialising in non-resident house owners.
Author: Gustavo Calero Monereo, lawyer at C&D Solicitors, Málaga